-
Liquid Data Mapper – Sub Functions
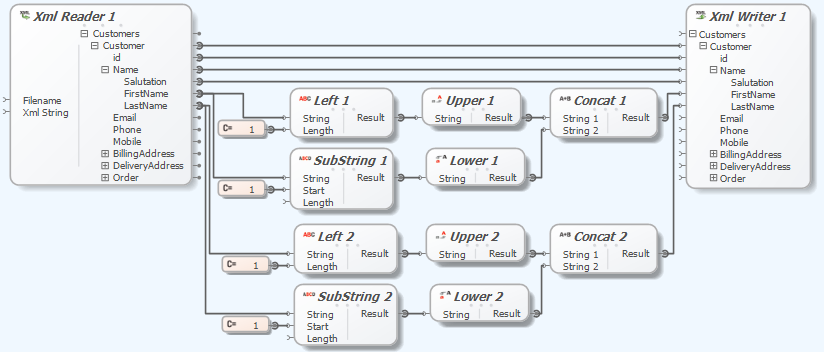
The Liquid Data Mapper simplifies complex data transformations, emphasizing the importance of Custom Sub Functions for maintainability and readability. An example illustrates transforming customer names by capitalizing the first letter. Sub Functions streamline the process, allowing reuse to enhance clarity.
-
Liquid Data Mapper – Dynamic Data Sources

The Liquid Data Mapper simplifies complex data transformations, enabling runtime loading of data sources like XML, JSON, CSV, and EDI documents. Users can dynamically combine files, as shown with XML examples where contents are merged.
-
Liquid Data Mapper – Duplicating Nodes
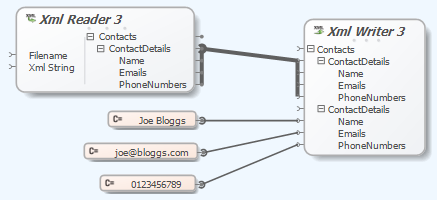
The Liquid Data Mapper simplifies complex data transformations by allowing users to connect multiple data sources. Users can duplicate nodes to merge data from various sources, such as XML files or constant values. This functionality enables efficient data integration, with a user-friendly diagram interface and debugging options for troubleshooting.
-
Liquid Data Mapper – Scalar Components

The Liquid Data Mapper facilitates complex data transformations by utilizing scalar components, which process single primitive values from sequences. Each scalar function can convert inputs sequentially, returning transformed values. Examples illustrate how components like ‘Upper’ and ‘Left’ work, producing evaluated sequences.
-
Liquid Data Mapper – Sequences

The Liquid Data Mapper enables efficient data transformations, utilizing sequences of values. Each connection point returns a sequence, even if it contains a single value or is empty. Examples illustrate how constant components generate sequences, which can be combined to create multiple elements in XML.
-
Liquid Data Mapper – Aggregate Functions

The Liquid Data Mapper simplifies complex data transformations by utilizing aggregate functions like Sum, Min, Max, Average, and Count. Each function operates within a specified context, allowing users to customize calculations based on datasets like BookStores. Adjusting contexts can change output, ensuring accurate totals for individual or combined stores.
-
Liquid Data Mapper – Filtering Data
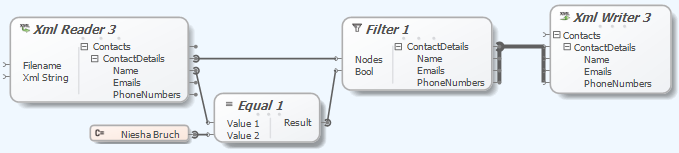
The Liquid Data Mapper facilitates quick and easy data transformations. It requires understanding basic concepts like filtering data, which uses a Boolean value to accept or reject nodes. An example demonstrates filtering XML data to create a new document with specific content.
-
Liquid Data Mapper – Sorting Data

The Liquid Data Mapper simplifies complex data transformations, starting with essential concepts like sorting data. Users can sort ContactDetails by name using ‘order by’ criteria in an XML source, dynamically determining output through input nodes.
-
Liquid Data Mapper – Data Manipulation

The Liquid Data Mapper simplifies complex data transformations. Users learn to read data from a source file, transform it, and write to a target file while converting ‘Name’ fields to uppercase. A drag-and-drop interface allows for easy manipulation, using XML data as an example.
-
Liquid Data Mapper – First Transform

The Liquid Data Mapper simplifies complex data transformations by requiring users to configure a target component from the Component Palette. Supported targets include databases, EDI, JSON, text files, web services, and XML. A simple example demonstrates generating an XML document.